
Patient Awareness
Colonoscopy
Minimally invasive test to detect changes or abnormalities in the large intestine (colon) and rectum.Polyps orother types of abnormal tissue
can be removed throughthe scope during a colonoscopy.
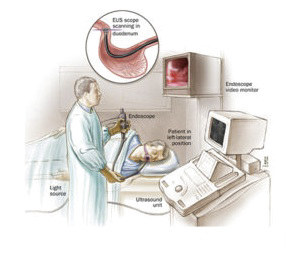
Endoscopic Ultra Sonography
Minimal invasive procedure in which endoscopy is combined with ultrasound to obtain images of the chest and digestive tract, adjacent organs and lymph nodes.EUS is performed on an OPD basis and is well-tolerated by most people
UGI Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a procedure that uses specialized tools to visualize and operate on the internal organs of the body. Endoscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic medical procedure.This procedure allows.

Pancreas
Pancreas is an organ situated in posterior aspect of the abdomen just above the level of umbilicus. It produces various substance having variety of functions in the body. It helps in digesting food, control the sugar level in the blood and other various functions.

Gall Bladder
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ which is adherent to the undersurface of the liver. It stores bile, a fluid that is made in the liver and helps in digesting fat.

Liver
The liver is a vital organ of vertebrates and some other animals.In the human it is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm

Esophagus
Esophagus is a hollow tube like muscular structure connecting mouth to the stomach and mainly resides in the neck and chest part of the body.

Stomach
The stomach is a hollow organ located just inferior to the diaphragm in the left part of the abdominal cavity. Located between the esophagus and the duodenum.

Duodenum
In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about 10-15 inches long connecting the stomach to the jejunum. It begins with the duodenal bulb and ends at the suspensory muscle of duodenum.

Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract between the stomach and the large intestine, The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum,jejunum, and ileum.

Large Intestine
large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon & rectum. the colon consists of four sections: the ascending colon, the transverse colon, the descending colon, and the sigmoid colon

Rectum
Rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in some mammals, and the gut in others. The human rectum is about 12 centimeters (4.7 in) long,and begins at the rectosigmoid

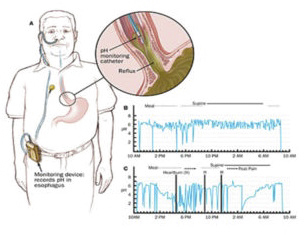
Manometry & PH Metry
Esophageal Manometry is a computerised instrument to know about the smooth functioning of food pipe in our body. The use of 24 hours pH metry is to diagnose the disease of acid reflux
What is Dyspepsia?
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, is a term used to describ5 one or more symptoms including a feeling of fullness during meal, uncomfortable fullness after a meal, and burning or pain in the upper abdomen. Indigestion is common in adults and can occur once in a while or as often as every day. Most people with indigestion experience more than one of the following symptoms:

What is an upper GI Endoscopy?
An upper GI endoscopy is a procedure to diagnose and treat problems in your upper GI (Gastrointestinal) tract. The upper GI tract includes your food pipe (esophagus), stomach, and the first part of your small intestine (the duodenum).

What is Colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is an exam used to detect changes or abnormalities in the large intestine (colon) and rectum.
During a colonoscopy, a long, flexible tube (colonoscope) is inserted into the rectum. A tiny video camera at the tip of the tube allows the doctor to view the inside of the entire colon

Chronic Constipation
Chronic constipation is infrequent bowel movements or difficult passage of stools that persists for several weeks or o longer. Though occasional constipation is very common, some people le experience chronic constipation that can interfere with their ability go about their daily tasks. Chronic constipation may also cause excessive straining to have a bowel movement.

What is Ulcerative Colitis?
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes long-lasting inflammation and ulcers (sores) in your large intestine. Ulcerative colitis affects the innermost lining (mucosal lining) of the large intestine (colon and rectum). Treatment can greatly reduce signs and symptoms of the disease and bring about long-term remission .However the patient in remission requires life long treatment and follow-up

What is Hepatitis B ?
Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). For some people, hepatitis B infection becomes chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. Having chronic hepatitis B increases your risk of developing cirrhosis — a condition that causes permanent scarring of the liver, liver failure or liver cancer.

What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common, chronic bowel disorder in which there is abdominal pain associated with change in consistency and frequency of stool. There are 3 different patterns of this disorder namely IBS- C (Constipation predominant) , IBS —D ( Diarrhoea predominant) and IBS — M ( Constipation + Diarhoea). The same patient can have different patterns at different times.

What is
Hepatitis C ?
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that usually causes chronic liver inflammation leading to serious liver damage. The hepatitis C virus (HCV) spreads through contaminated blood, contaminated syringe & unprotected sex. Can also rarely be transmitted from mother to foetus during delivery.

What is Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)?
Gastroesophageal reflux is a physical condition in which acid from the stomach flows backward up into the esophagus. people will experience heartburn when excessive amounts of acid from the stomach refluxes into the esophagus.

